
In the world of heavy industry, the smallest component can bring the mightiest machines to a grinding halt. Bearings, though tiny compared to the equipment they support, play a pivotal role in ensuring uninterrupted operations. When these bearings fail, the consequences can be severe, leading to costly downtime and significant repair expenses. This blog post dives into why bearing wear investigations are essential, especially through the lens of a recent RTP project, to exemplify their impact on heavy industry.
Understanding Bearing Wear and Its Impact on Equipment Performance
Bearings are the heart of most machines, facilitating smooth rotations and reducing friction. Equipment that uses bearings, whether rotary or linear, includes anything that turns or slides during operation. Some specific items RTP has recently worked with include sliding doors, trim press roll-over tables, fans, rolling mills, and roll conveyors. However, when bearings wear out, they can cause machinery to stop, often leading to extensive investigations to find the root cause. According to Schaeffler, 85% of bearing failures are preventable, making it crucial for industries to understand and address the underlying issues, such as material fatigue, misalignment, and improper lubrication.
The Basics of Bearing Wear
Bearing wear can manifest in various forms, including small cracks, spalling, and abnormal surfaces. These issues often result from material fatigue, which can occur on the surface or subsurface. Preventable wear is typically caused by abrasive and adhesive wear, while corrosion, identified by red/brown stains or brown/black etching, results from moisture exposure or fretting. Understanding these signs is essential for diagnosing and preventing future failures.
The Dangers of Bearing Failure
Bearing failure is a complex subject involving metallurgy, tribology, operating environment, and applied loads. Sometimes a single event can cause a failure, while other times, multiple factors contribute to the issue. These factors can include poor human decisions, harsh environmental conditions, severe operational settings, and inadequate maintenance practices. All these elements can lead to premature failure.
Ultimately, this results in catastrophic failure of the rotating or reciprocating component and can cause additional damage to associated mechanisms. Given the high cost of lost production and the time constraints on maintenance teams, it is crucial to simplify and expedite the problem-solving process.
Impact on Equipment Performance
When bearings fail, the performance of the entire machine is compromised. Symptoms like overheating, abnormal wear paths, and discoloration indicate deeper issues that need addressing. For instance, an overheating bearing may result from insufficient lubrication, leading to blue discoloration on raceways. Similarly, misalignment can cause an abnormal ball wear path, affecting the machine's overall efficiency.
The Role of Root Cause Failure Analysis
RCFA is a systematic approach to identifying the underlying causes of bearing failures. By examining factors such as cracks, surface fatigue, and lubrication issues, industries can implement corrective measures to prevent recurrence. Let's explore the key aspects of RCFA in bearing wear investigations.
Identifying Cracks and Spalling
Tiny cracks and micro-spalling are often indicators of material fatigue. Subsurface-initiated fatigue and surface-initiated fatigue are common types that need addressing. Detecting these early can prevent more significant damage and extend the lifespan of the bearings.
Recognizing Dull or Shiny Surfaces
Abrasive and adhesive wear can cause surfaces to appear abnormally dull or shiny. Identifying these signs helps in diagnosing the factors contributing to premature wear, such as improper lubrication or contamination.
Corrosion and its Causes
Red/brown stains or brown/black etching in rolling elements signify corrosion, often due to moisture exposure or fretting erosion. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further degradation of the bearings.
A Look into a Recent RTP Bearing Investigation
A heavy industrial client approached RT Patterson with a recurring problem of premature bearing failures in OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) supplied equipment. Despite an initial improvement that extended the Mean Time to Failure (MTTF) to 18 months, the issue persisted. RTP's investigation revealed two primary causes: oscillating motion causing lubricant voids and metal-to-metal contact, and inherent misalignment leading to axial binding.
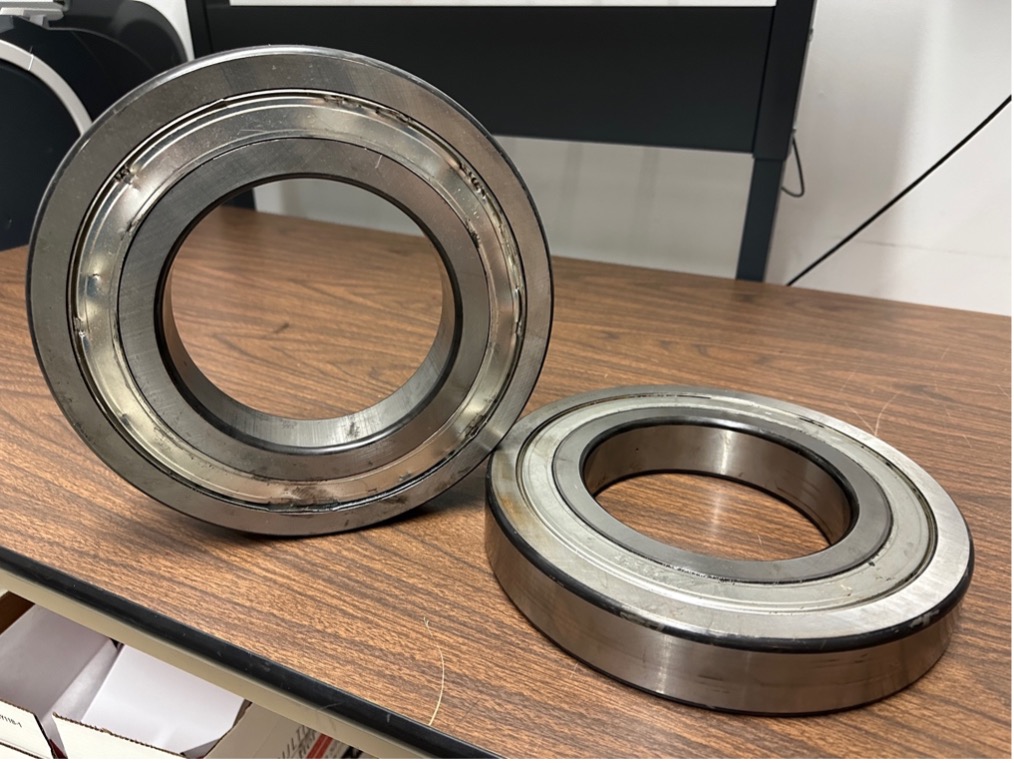

(Original OEM Bearings)
Equipment History
The client’s equipment comprised a U-shaped rotating table supported by two stub shafts and two bearing housings. Each stub shaft held two bearings enclosed in bearing housings, featuring inboard grease seals on both ends and an outboard seal solely on the idler shaft. The equipment also included a splined shaft gearbox with a hydraulic motor attached to the driven end, which lacked a bearing seal. The rollover table was powered by a hydraulic motor/gearbox setup with valves, enabling it to rotate 180 degrees clockwise and counterclockwise at speeds between 8-12 RPM, cycling every 90 seconds. The interface of the table had five bolted connections between the bearing surfaces on each shaft and three bolted and keyed connections per bearing mounting surface.
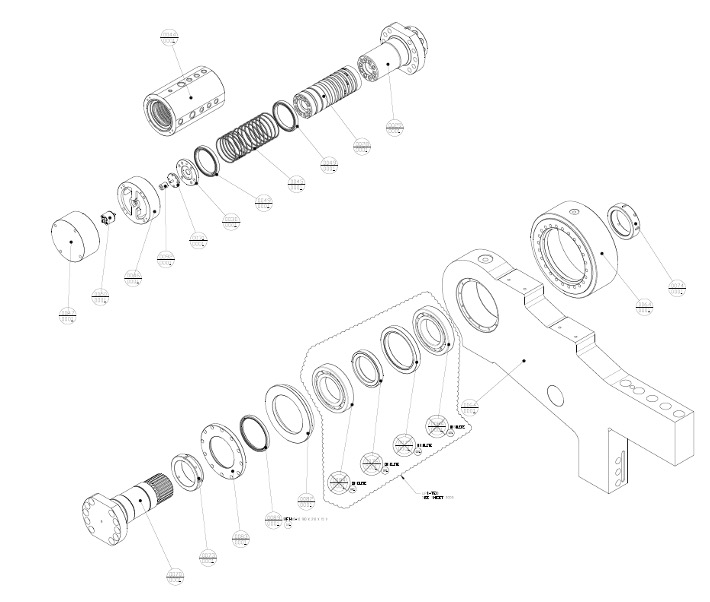
(Original OEM Bearing Assembly)
Originally, the equipment utilized deep groove ball bearings provided by the OEM, which had an MTTF (Mean Time to Failure) of typically only three months, attributed to pre-packed lubrication during manufacture. Following failures, the bearings were replaced with those pre-packed with Chevron-Mulifak EP-1 grease and fitted with external shaft seals. This replacement extended the MTTF to 18 months, still short of the customer’s expectations. Upon analysis, RTP identified potential for significantly increased MTTF, surpassing the OEM's best improvement.
R.T. Patterson Study Details
RTP’s comprehensive investigation centered on several critical-to-quality (CTQ) elements:
- Lubrication Retention: Absence of shaft seals for retaining bearing lubricant.
- Alignment and Axial Loading: Ensuring alignment of bearing housings and mitigating axial loads caused by thermal expansion.
- Documentation and Damage: Examination of OEM documentation, bearing race damage from installation, nearby equipment vibrations, and environmental factors.
- Lubrication Suitability: Evaluating lubrication properties specific to the oscillating motion application.
- Loading Conditions: Analysis based on loading scenarios derived from operational data, ensuring calculations adhered to safety factors.
Using data on bearing models, specifications, lubricants, reaction forces, and more, RTP performed static stress calculations. They identified critical load conditions under various scenarios, recommending a safety factor of 2 for permissible static load. Calculations demonstrated that the existing MTTF could be exponentially improved, with factors significantly higher than the actual failures experienced.
Study Exploration of Possible Failure Modes
RTP explored multiple potential failure modes, including:
- Lubrication Failure: Detrimental effects of oscillation on lubricant boundary conditions and metal-to-metal contact due to lack of lubrication.
- Misalignment and Axial Loads: Severe radial and axial loads stemming from misaligned bearings and additional axial loads.
- Shock Impacts: Impact damage from process downstrokes and errant scrap pieces during operations.
- Bearing Installation Damages: Impact forces during installation causing surface dents leading to spalling.
- Environmental Effects: Potential negative effects of humidity and temperature on lubrication performance.
Study Field Notes and Conclusions
Field observations indicated that bearing failure was likely due to a combination of lubrication failure, bearing misalignment, and added axial loads. Large metal scrap pieces causing operational upsets also contributed to higher dynamic and static loads on the bearings, leading to rapid deterioration.
Study Recommendations and Solutions
Based on these findings, RTP proposed the following measures to rectify the bearing issues:
- Bearing Replacement: Utilize self-aligning spherical roller bearings.
- Spacer Redesigns: Implement redesigned spacers for both idler and driven ends.
- Grease Seals and Housing Modifications: Incorporate grease seals on the motor side and modify housings for external lubrication.
- Auto-Lubrication Systems: Install single-point auto-lube units for consistent lubrication.
- Optimized Lubricant: Switch to a lubricant formula suitable for oscillating motion.
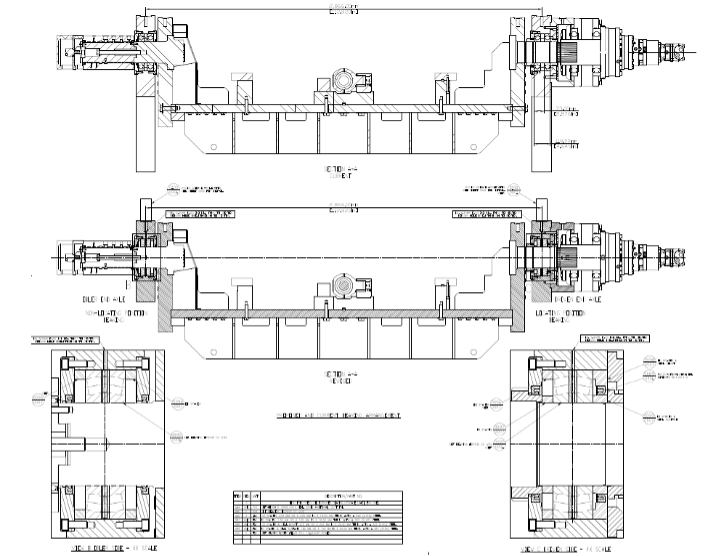
(Bearing Assembly Showing Revisions)
With the RT Patterson design improvements implemented, significant gains in bearing life were already realized, outperforming any previous MTTF recorded. The customer has also realized lowered maintenance costs and extended production time without unplanned outages, thus meeting their expectations for RT Patterson’s promise on providing a tangible solution for their equipment issues.
Benefits of Implementing Bearing Wear Investigations
Implementing bearing wear investigations offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it enhances equipment reliability, ensuring continuous operations and minimizing downtime. Secondly, it reduces maintenance costs by extending the lifespan of machinery components. Lastly, it improves safety by preventing unexpected mechanical failures.
By investing in bearing wear investigations, industries can achieve higher productivity levels and maintain a competitive edge. The RTP project exemplifies how targeted solutions can address specific issues and lead to significant improvements in machinery performance.
Conclusion
Bearing wear investigations are not just a maintenance task but a strategic investment in the long-term success of heavy industries. By understanding the root causes of bearing failures and implementing targeted solutions, industries can achieve higher reliability, reduced costs, and improved safety. Remember, bearings usually don’t fail us. We fail them.
The RTP project serves as a testament to the effectiveness of comprehensive bearing wear investigations. By proactively addressing bearing wear, industries can ensure continuous operations, minimize downtime, and maintain a competitive edge in the market. Investing in bearing wear investigations is an investment in the future of your industry. To learn more about how RTP's solutions can benefit your operations, reach out to our team today.